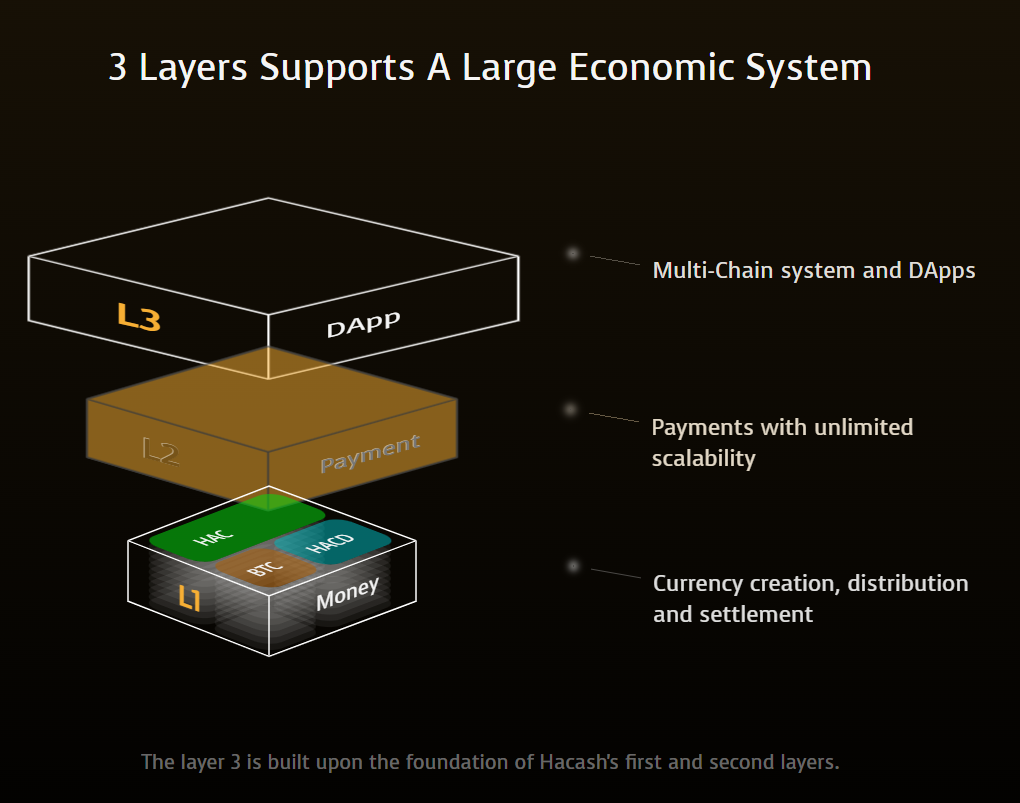
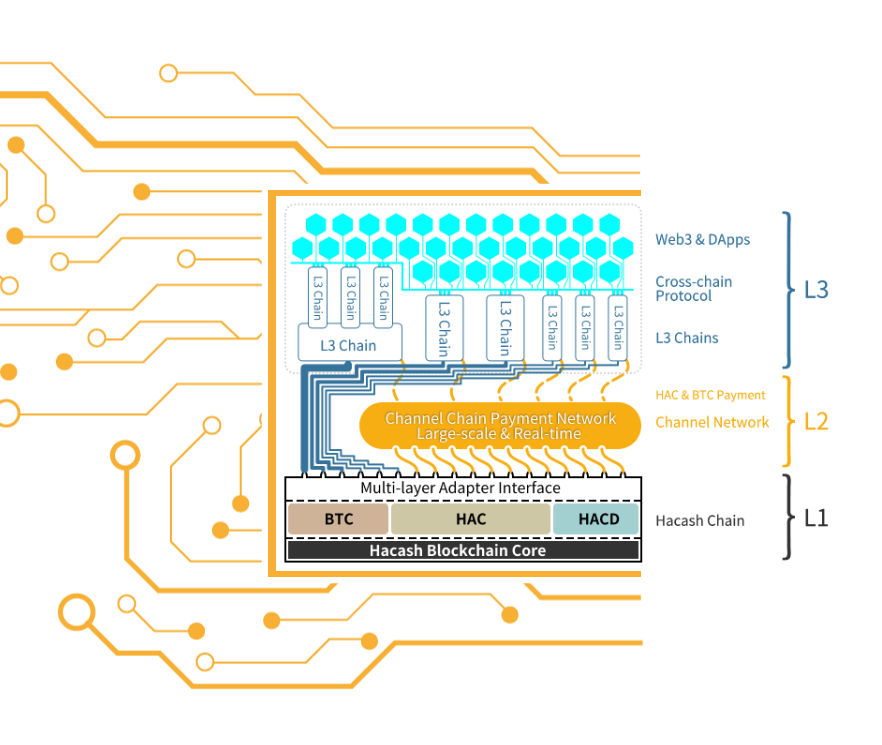
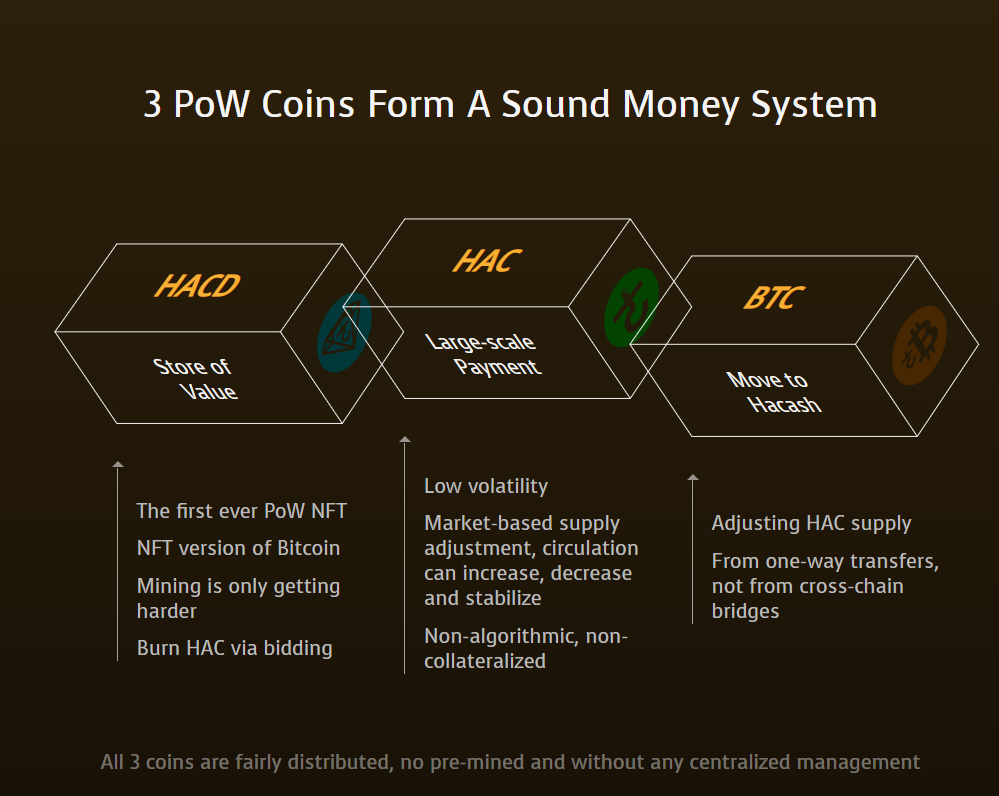
4.1 Basic Data Structures
Three-level hierarchy: Blocks >> Transactions >> Actions. Simple, human-readable, compact format for both machine and human verification. Transactions contain: actions (operations), signs (individual signatures), multisigns (multi-signature data).
4.2 Multisignature Addresses
Support for 2/2, 1/2, 2/3, 1/3 configurations and more. Multiple private keys manage single addresses. Up to 200 private keys can manage one multisignature address. No single secret key; security distributed across key holders.
4.3 Hierarchical Equity Control Accounts
Support modern corporate structures with beneficiary and voting rights. Features: jointmanagement, dynamic key changes, changeable voting ratios, different rights per equity, fund protection in extreme cases (collective key loss scenarios).
4.4 Multi-Signature Transactions
Atomic operations requiring multiple signatures. If one action fails, all fail. Prevents fraud in equity investments and complex financial operations where both parties must simultaneously commit.
4.5 Payment Categories
Support for diverse payment types: self-pay, payment requests, delegated payments, and equity operations. Different contract structures for different business scenarios.
4.6 Signature Stripping
Signatures occupy significant block space. After sufficient confirmation (1+ year), signature data can be stripped from historical transactions while maintaining core transaction data, reducing blockchain size dramatically.
4.7 Transaction Fees
Fees collected by miners create economic incentive for participation. Fluctuate based on network congestion. Can be zero or negative (subsidies). Fee payer's signature separated from other participants.
4.8 Field Formats
Standardized formats for transaction data using scientific notation for monetary amounts, ensuring consistency and efficiency across the network.